Context: Social/Cultural World of Jesus
The political situation of first century Jewish Palestine was a domination system marked by peasant society, purity society, and patriarchal society.
~ Marcus Borg
Political dimension
Jesus lived in Jewish Palestine in the first century. This is the historical/cultural/social context in which he must be understood.
 At
that time, Palestine was part of the Roman empire, under the domination
of a foreign empire.
At
that time, Palestine was part of the Roman empire, under the domination
of a foreign empire.
Rome ruled indirectly:
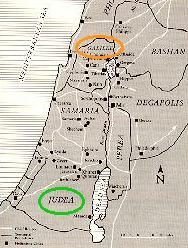
Galilee:
- In the north
- Ruled by Herod Antipas (son of Herod the Great)
- Herod owed his appointment to Rome
Judea:
- In the south
- Ruled by a circle of the Jewish aristocratic elite
- These elite collaborated with the Roman government
This domination system was marked by:
- Peasant Society
- Purity Society
- Patriarchal Society
Peasant Society
 Peasant
society refers to a pre-industrial agrarian society where:
Peasant
society refers to a pre-industrial agrarian society where:
- Peasant agricultural production is the only real source of wealth
- There is no manufacturing
- There is no industry except small scale handcrafts
Peasant societies are marked by an enormous gulf between rural peasants and urban ruling elites.
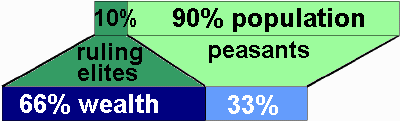
The urban ruling elites (king, aristocratic families, high government officials) and retainers (servants, army, lower government officials, religious officials):
- Comprise 10% of population
- Extract 66% of the value of rural production through:
- Taxation: civil and religious (tithes are taxes on agricultural produce to be paid to the temple authorities)
- Land rent: direct payment or sharecropping
- Are enormously wealthy in the standards of the day
- Don’t produce anything and hardly provide any services except an army for warfare
Peasant society was politically oppressive, economically exploitative, and religiously legitimated.
Purity System
The central social structure of the society was organized with purity as the core value. Purity systems generate a class of untouchables and outcasts.
Purity was the core value structuring the society:
- Purity was not an individual virtue
- Purity was political
- It was the ideology of the temple elites
- The Jerusalem temple was geographically and symbolically the center of the purity system
In general the pure/impure or clean/unclean social structure got attached to other central contrasts:
| Pure | Impure |
|---|---|
| clean | unclean |
| righteous | outcasts, sinners (sin is a matter of being unclean, not behavior) |
| male (generally but not automatically pure) |
female (automatically impure) |
| rich (generally but not automatically pure) |
poor (conventional wisdom said the poor hadn't lived right) |
| Jew (generally but not automatically pure) |
gentile (impure by definition) |
| well/healthy/whole | ill/maimed/diseased (social meaning of being impure) |
| agricultural produce on which taxes were paid | agricultural produce on which taxes were not paid (declared unclean, boycotted by the righteous) |
The purity system creates a society with very sharp social boundaries.
The temple elites were also the economic elites and the purity elites.
 Patriarchal
Society
Patriarchal
Society
Patriarchal society is:
- Male dominated
- Hierarchical
- Mirrored in the family structure
It is crucial to see the centrality of the temple and the temple aristocracy in the whole system because of the centrality of the temple in the world of Jesus’ life.
Questions to ponder...
Domination systems, such as that in Jesus’ lifetime, exist today.
What are some domination systems you know about or have experienced?
Jesus stands in the tradition of the prophets of Israel who criticized their culture in the name of God and became voices of an alternative consciousness.
